While the Bitcoin Protocol laid the foundation for a new era of peer-to-peer financial services when it was launched in 2009, Ethereum, the first smart contracts-powered blockchain and the platform on which the Maker Protocol is built, offers the ability to execute the kind of complex functionality required by modern finance applications.
Today, nearly six years after its launch, the Ethereum blockchain hosts an over $42 billion ecosystem of decentralized applications that provide wide-ranging services previously available only to wealthy or institutional investors.
DeFi is an open and global financial system built for the internet age — an alternative to a system that’s opaque, tightly controlled, and held together by decades-old infrastructure and processes. Decentralized Finance is a blockchain-based form of finance that does not rely on central financial intermediaries such as brokerages, exchanges, or banks to offer traditional financial instruments, and instead utilizes smart contracts on blockchains, the most common being Ethereum.
DeFi platforms allow people to lend or borrow funds from others, speculate on price movements on a range of assets using derivatives, trade cryptocurrencies, insure against risks, and earn interest in savings-like accounts. DeFi uses a layered architecture and highly composable building blocks. Some DeFi applications promote high interest rates but are subject to high risk.
By October 2020, over $11 billion (worth in cryptocurrency) was deposited in various decentralized finance protocols, which represented more than a tenfold growth during the course of 2020. As of January 2021, approximately $20.5 billion was invested in DeFi.
Non-Custodial
These distributed networks allow people to have control over their own assets and data and for value to be transferred from one person to another, without the need to use intermediaries like banks and other financial institutions. Users are the only ones who hold the keys to their wallets and control their funds. The term used to describe this feature is that DeFi apps are “non-custodial,” as they don’t have custody of your assets — you do.
Open
These networks are also global, which means there are no borders in this parallel financial system, and everyone can access it. It’s like the internet, but instead of information being transferred globally, seamlessly and creatively, the same is happening with money. It’s an internet of value.
Transparent
The code for these financial applications is open for anyone to see and inspect. This is important because anyone is able to verify how the applications and protocols work, and track exactly where their money is.
Composable
Open-source code also enables developers to build on top of others’ applications, accelerating innovation and allowing these applications to become like lego pieces, leveraging each others’ value — hence the term, “money legos.” And if users don’t like how one application is being built, they can copy the code and build a new app.
Decentralized
DeFi protocols are built on public blockchains like Ethereum. These blockchains, the rails to this new financial system, are run by thousands of nodes — computers running the blockchain’s software — spread out across the globe, so that it’s almost impossible to censor or stop them.
On top of this base layer of decentralization, DeFi platforms are built to be managed by a community of users, and not centrally controlled. Users become owners of their financial applications; they’re able to participate in major decisions, including by proposing changes themselves, and benefit from their growth and success. No centralized party can unilaterally take control of funds or change the rules of the game.
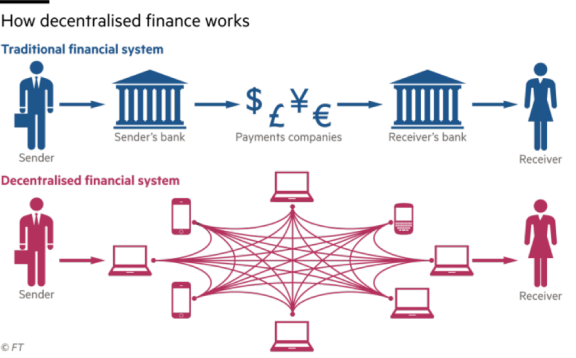
Please look at infographic provided below to better understand the difference between DeFi, Traditional Finance, and FinTech.

One could argue that DeFi started with Bitcoin in 2009. BTC was the first-ever peer-to-peer digital money; the first financial applications built on blockchain technology.
But the turning point for financial applications allowing users to do more with their money than send it from point A to point B happened in December 2017, when MakerDAO launched.
MakerDAO is an Ethereum-based protocol that allows users to issue a cryptocurrency that’s pegged at 1-to-1 to the value of the U.S. dollar by using digital assets as collateral. This mechanism effectively allowed anyone to borrow the Dai stablecoin against Ether (Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency). It created a way for anyone to take out a loan without relying on a centralized entity. It also created a dollar-pegged digital asset, which didn’t rely on holding dollars in a bank, like USDC, USDT and other stablecoins.
The MakerDAO lending protocol and its Dai stablecoin provided the first building blocks for a new, open, permissionless financial system. From there, other financial protocols launched, creating an increasingly vibrant and interconnected ecosystem. Compound Finance, released in September 2018, created a market for borrowers taking out collateralized loans, and lenders to rake in interest rates paid by those borrowers. Uniswap, launched in November 2018, allowed users to seamlessly and permissionlessly swap any token on Ethereum.
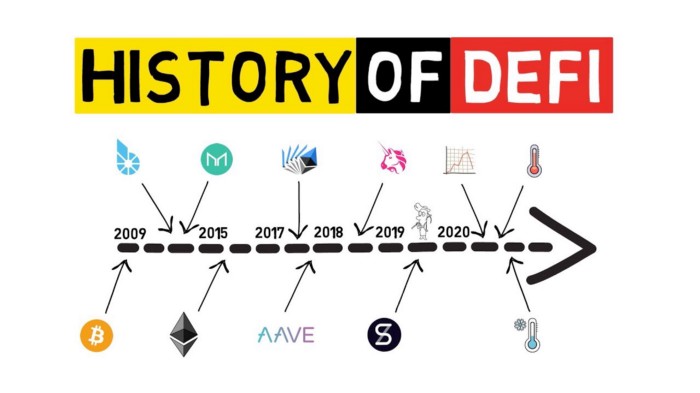
Less than three years after MakerDAO placed the first money lego, there are now dozens of DeFi applications, from basic use-cases like enabling lending, borrowing, trading, to crazier ones like creating synthetic assets, streaming payments and playing in a lottery where you can always get your money back.
Assets held in these platforms’ smart contracts climbed to surpass $1 billion, then quickly $2, $3 and $4 billion just this year. It’s clear we’re just getting started.
DeFi uses cryptocurrencies and smart contracts to provide services that don’t need intermediaries. In today’s financial world, financial institutions act as guarantors of transactions. This gives these institutions immense power because your money flows through them. Plus billions of people around the world can’t even access a bank account.
In DeFi, a smart contract replaces the financial institution in the transaction. A smart contract is a type of Ethereum account that can hold funds and can send/refund them based on certain conditions. No one can alter that smart contract when it’s live — it will always run as programmed.
A contract that’s designed to hand out an allowance or pocket money could be programmed to send money from Account A to Account B every Friday. And it will only ever do that as long as Account A has the required funds. No one can change the contract and add Account C as a recipient to steal funds.
Contracts are also public for anyone to inspect and audit. This means bad contracts will often come under community scrutiny pretty quickly.
This does mean there’s currently a need to trust the more technical members of the Ethereum community who can read code. The open-source based community helps keep developers in check, but this need will diminish over time as smart contracts become easier to read and other ways to prove trustworthiness of code are developed.
When talking about DeFi, these 3 words will eventually pop up in my head — cryptography, decentralization, and blockchain. It is a financial system concept which has several value propositions:
No single authority can disrupt the market. This reduces the chance of fraud or injustice done by bad actors in the financial system (such as the famous GameStop and WallStreetBets case)
Interest rates adjusted automatically based on supply, demand, and risk parameters.
Accounting becomes super easy, most likely will be completely automated in the future. This will reduces operating cost significantly.
Personally, I believe in DeFi. I believe that this concept will become the main financial system in the future, or at least supplement the current one. I also agree with Vitalik Buterin’s statement at Ethereal Summit 2020. Everyone should have equal access to financial system and the services it provides, no matter who they are and where they are.
”I’m very excited about the potential DeFi offers in principle. The idea that just anyone, anywhere in the world, can have access to a system that lets them pay each other, and choose their own financial exposure, is a really powerful thing. It’s something that a lot of people don’t have access to.” — Vitalik Buterin, Co-founder of Ethereum
<100 subscribers